Incubadora de Placas de Petri
Objetivo
O objetivo desse projeto é criar uma incubadora para cultivo de microorganismos em placas de petri. Com esse equipamento é possível garantir o crescimento nas melhores condições controladas para diferentes tipos de microrganismos. Uma incubadora é um dos equipamentos essenciais para qualquer laboratório de microbilogia ou biologia molecular.
Design
O design da incubadora foi feito para uma estrutura de mdf de 3mm de espessura com encaixes para parafusos de máquina de 10 mm de comprimento e 3,4 mm de diâmetro. O design é baseado no projeto "Incubator" da Biohack Academy e as partes em mdf foram cortadas no Garagem FAB Lab. Uma mudança da funcionalidade do design original foi a colocação de coolers para resfriamento do interior da incubadora caso necessário.
Modelo 3D
O modelo 3D da incubadora foi feito em sketchup. O modelo e sua planificação estão disponíveis para download aqui:
Debugando o Hardware
Após cortar na laser percebeu-se que as medidas cortadas foram cerca de 10% maiores do que o esperado. O plano era aproveitar uma caixa de isopor para ser o isolante. Por causa disso foi preciso arrumar placas avulsas de isopor de espessura adequada, o que deu um pouco mais de trabalho. É importante tomar cuidado com as importações para dxf à partir do sketchup. Usamos esse plugin.
A dobradiça em mdf é bonitinha mas quebra com facilidade. É melhor usar uma dobradiça comercial facilmente encontrável por aí - aproveite e compre uma tranca simples também.
Eletrônica e Elétrica
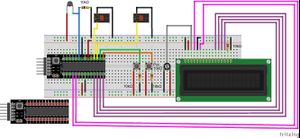
Usamos um dos clones brasileiros do Arduino mais mão-na-roda do mercado, o Garagino rev1, montando todo o circuito em protoboard. O controle todo é muito simples: um relê controlando o par de coolers de resfriamento, um relê controlando o liga-e-desliga da lâmpada incandescente (que é fonte de aquecimento), um termistor (foi usado um termistor bem não-convencional por questões de disponibilidade, esse aqui) medindo a temperatura, dois botões e um LCD.
O esqueminha eletrônico construído foi o seguinte:
O código Arduino escrito:
- include <LiquidCrystal.h>
- include <math.h>
//Variables//
//Electronic system configuration
int thermistorPin = A0; // Pin where the thermistor is connected
int minusButton = 9; // Pin where the menu temperature decreasing button is connected
int plusButton = 10; // Pin where the menu temperature increasing button is connected
int fanRelay = 11; // Pin where the Relay Module for controlling the fans is connected
int lampRelay = 12; // // Pin where the Relay Module for controlling the heating lamp is connected
LiquidCrystal lcd(2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8);
//Operational variables
int standardTemp = 25; // Initial temperature of the Incubator
int maxTemp = 45; // for safety precautions, 45 celsius is the largest value the incubator may have
int minTemp = 20; // temperature arbitrary defined for the minimum temperature setting allowed
int maxHeat = 2; // maximum temperature difference allowed for the current temperature to be higher than the defined by the user
int refreshingRate = 500; // Milliseconds that each loop waits for checking the temp and if the buttons are pressed
//Temperature equation constants
double Beta = 3435; // Beta value (or "B" value) from the thermistor, using the Beta parameter equation, a particular case of the Steinhart–Hart equation for thermistors
double R25 = 10000; // Resistance of the thermistor at 25 celsius
double Ref = 10000; // Resistance of Reference from the Voltage Divider Circuit (10K for example)
//Functions//
void CheckButtons(int plus, int minus){ // Checks if the user press-and-holded one of the two buttons and changes the standardTemp variable. Also refresh the LCD screen for the target temperature
while(digitalRead(plus) == HIGH){ //while the user is pressing the button the target temperature is incremented
if(standardTemp == maxTemp){ // if the standardTemp reaches the maximum temperature allowed it is not incremented anymore
break;
}
standardTemp++;
lcd.setCursor(9, 0);
lcd.print(standardTemp, DEC);
delay(300); // this defines how fast the numbers being set on the LCD screen are changed
}
while(digitalRead(minus) == HIGH){ //while the user is pressing the button the target temperature is decremented
if(standardTemp == minTemp){ // if the standardTemp reaches the minimum temperature allowed it is not decremented anymore
break;
}
standardTemp--;
lcd.setCursor(9, 0);
lcd.print(standardTemp, DEC);
delay(300); // this defines how fast the numbers being set on the LCD screen are changed
}
}
double MeasureResistance(int ARead){ // Transforms pwm values of thermistorPin in voltage and calculates the thermistor resistance by the voltage divider equation
double Rtherm = ((5.0*Ref)/(ARead*(5.0/1023.0))) - Ref;
return Rtherm;
}
int CalculateTemp(double resistance){ //Given the resistance value of the thermistor, returns the temperature by using the thermistor equation for termperature
double T = ((298.0*Beta)/(298.0*log(resistance/R25) + Beta)); // Beta parameter equation, a particular case of the Steinhart–Hart equation for thermistors. Temperature of reference is 25 Celsius.
T = T-273; // converts Kelvin to Celsius
return T;
}
byte degree[8] = { //Generates the "degree" character of the Celsius representation on the LCD screen
B00111,
B00101,
B00111,
B00000,
B00000,
B00000,
B00000,
};
void setup() {
// LCD stetup //
lcd.begin(16, 2);
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("Target:");
lcd.setCursor(11, 0);
lcd.write(byte(degree[8]));
lcd.print("C");
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("Status:");
lcd.setCursor(11, 1);
lcd.write(byte(degree[8]));
lcd.print("C");
// Pins Setup //
pinMode(plusButton, INPUT);
pinMode(minusButton, INPUT);
pinMode(fanRelay, OUTPUT);
pinMode(lampRelay, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
//Data gathering//
CheckButtons(plusButton, minusButton); //Checks for new user inputs
double Rvalue = MeasureResistance(analogRead(thermistorPin)); // The Voltage measured on thermistorPin is converted to Resistance by measureResistance and the temperature is given by calculateTemp, then the LCD is refreshed
int Temp = CalculateTemp(Rvalue); // Returns, in Celsius, the current temperature value;
lcd.setCursor(9, 1);
lcd.print(Temp, DEC); //LCD current temperature refreshing
//Incubator Controlling//
if(Temp < standardTemp){ // if the current temp is lower than the target, it turns on the lamp
digitalWrite(lampRelay, HIGH);
if(digitalRead(fanRelay) == HIGH){ // in case the cooling fans were on, they're shut down
digitalWrite(fanRelay, LOW);
}
}
if(Temp > standardTemp){ // if the current temp is higher than the target, it turns off the lamp
digitalWrite(lampRelay, LOW);
if(Temp >= standardTemp + maxHeat){ // in case the current temperature is too high (defined by maxHeat), the cooling fans are turned on
digitalWrite(fanRelay, HIGH);
}
}
if(Temp == standardTemp && digitalRead(lampRelay) == HIGH){ // in case the current temperature matches the one defined by the user and the lamp is on, it turns it off
digitalWrite(lampRelay, LOW);
}
if(Temp == standardTemp && digitalRead(fanRelay) == HIGH){ // in case the current temperature matches the one defined by the user and the fans are on, it turns them off
digitalWrite(fanRelay, LOW);
}
delay(refreshingRate); //time the microcontroller stays idle until the next check and controlling cycle
}